In the ever-advancing landscape of healthcare, medical instruments play a pivotal role in diagnosing and monitoring various conditions. Among these, the Aneroid Sphygmomanometer stands as a fundamental tool for measuring blood pressure. This article explores the evolution, functionality, and significance of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers in contemporary healthcare settings.
I. Historical Perspective
A. Origin and Development
The Aneroid Sphygmomanometer has a rich history that traces back to the 19th century. Invented by Samuel Siegfried Karl Ritter von Basch in 1881, this innovative device marked a departure from its mercury-based predecessor. The Aneroid Sphygmomanometer replaced the cumbersome and hazardous mercury columns with a more portable and user-friendly mechanism, setting the stage for its widespread adoption.
B. Advancements Over the Years
Since its inception, the Aneroid Sphygmomanometer has undergone significant improvements. Early versions were often delicate and required frequent calibration. However, advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have led to the development of sturdier and more reliable models. These improvements have contributed to the widespread use of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers in clinical settings and homes alike.
II. How Aneroid Sphygmomanometers Work
A. Mechanical Components
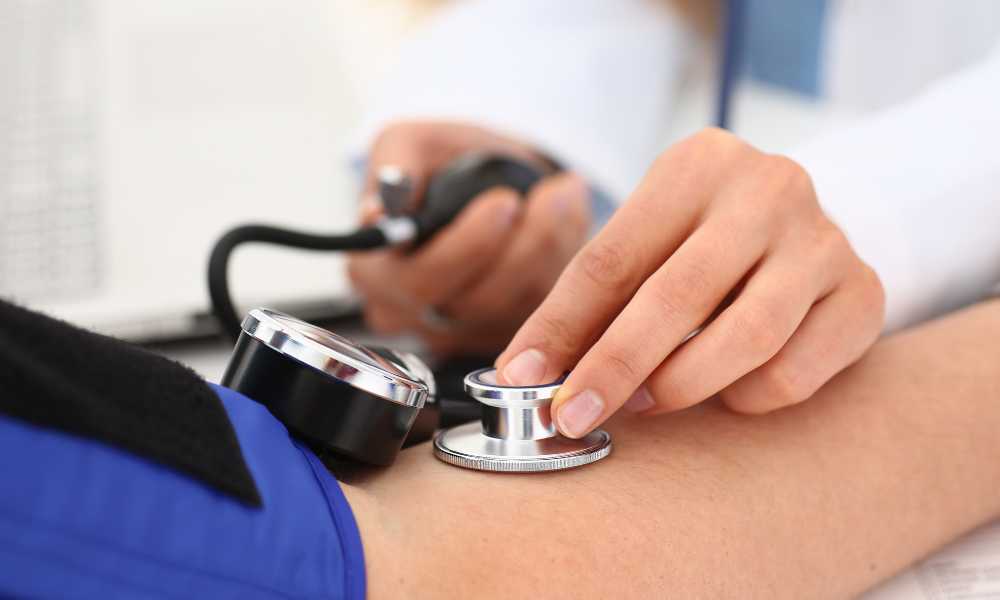
The Aneroid Sphygmomanometer consists of several key components, each playing a crucial role in its functionality. These include a cuff, an inflation bulb, a pressure control valve, and the aneroid gauge. The cuff wraps around the patient’s arm, and when inflated, it temporarily stops the blood flow. The pressure control valve regulates the release of air, and the aneroid gauge provides the blood pressure reading.
B. Operation Process
To measure blood pressure using an Aneroid Sphygmomanometer, the healthcare professional or user wraps the cuff around the upper arm, positioning it over the brachial artery. The inflation bulb is then squeezed to increase the pressure within the cuff, temporarily stopping blood flow. As the pressure is released slowly, the healthcare professional listens for the characteristic sounds of blood flow with a stethoscope. The corresponding pressure level is noted when the sounds are first heard (systolic pressure) and when they disappear (diastolic pressure).
III. Advantages of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers
A. Portability and Convenience
One of the primary advantages of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers is their portability. Unlike their mercury counterparts, aneroid devices are compact and lightweight, making them suitable for use in various healthcare settings, including clinics, hospitals, and even in-home monitoring.
B. Accuracy and Precision
Aneroid Sphygmomanometers are known for their accuracy when used correctly. Regular calibration and maintenance ensure that these devices provide precise blood pressure readings. This accuracy is crucial for the effective management of hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions.
IV. The Role of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers in Healthcare
A. Routine Blood Pressure Monitoring
Regular blood pressure monitoring is essential for the prevention and management of cardiovascular diseases. Aneroid Sphygmomanometers play a vital role in this process, enabling healthcare professionals to assess a patient’s blood pressure accurately during routine check-ups or emergency situations.
B. Home Blood Pressure Monitoring
The compact and user-friendly nature of Aneroid Sphygmomanometers makes them suitable for home use. Many individuals with chronic conditions, such as hypertension, rely on these devices to monitor their blood pressure regularly. This self-monitoring empowers patients to actively participate in their healthcare and allows for early detection of potential issues.
V. Challenges and Considerations
A. Calibration and Maintenance
While Aneroid Sphygmomanometers offer accuracy, they require regular calibration and maintenance to ensure consistent performance. Improper calibration or neglect of maintenance can lead to inaccurate readings, potentially impacting patient care.
B. Skill-dependent Measurements
Unlike automated blood pressure monitors, using an Aneroid Sphygmomanometer requires a certain level of skill and training. Healthcare professionals must be adept at listening for the characteristic sounds using a stethoscope and interpreting the readings accurately.
Conclusion
The Aneroid Sphygmomanometer has come a long way since its inception, evolving into a crucial tool in the field of healthcare. Its portability, accuracy, and role in routine and home blood pressure monitoring make it an indispensable instrument for medical professionals and individuals alike. As technology continues to advance, the Aneroid Sphygmomanometer remains a steadfast and reliable companion in the quest for better cardiovascular health.